 Image 1 of 7
Image 1 of 7

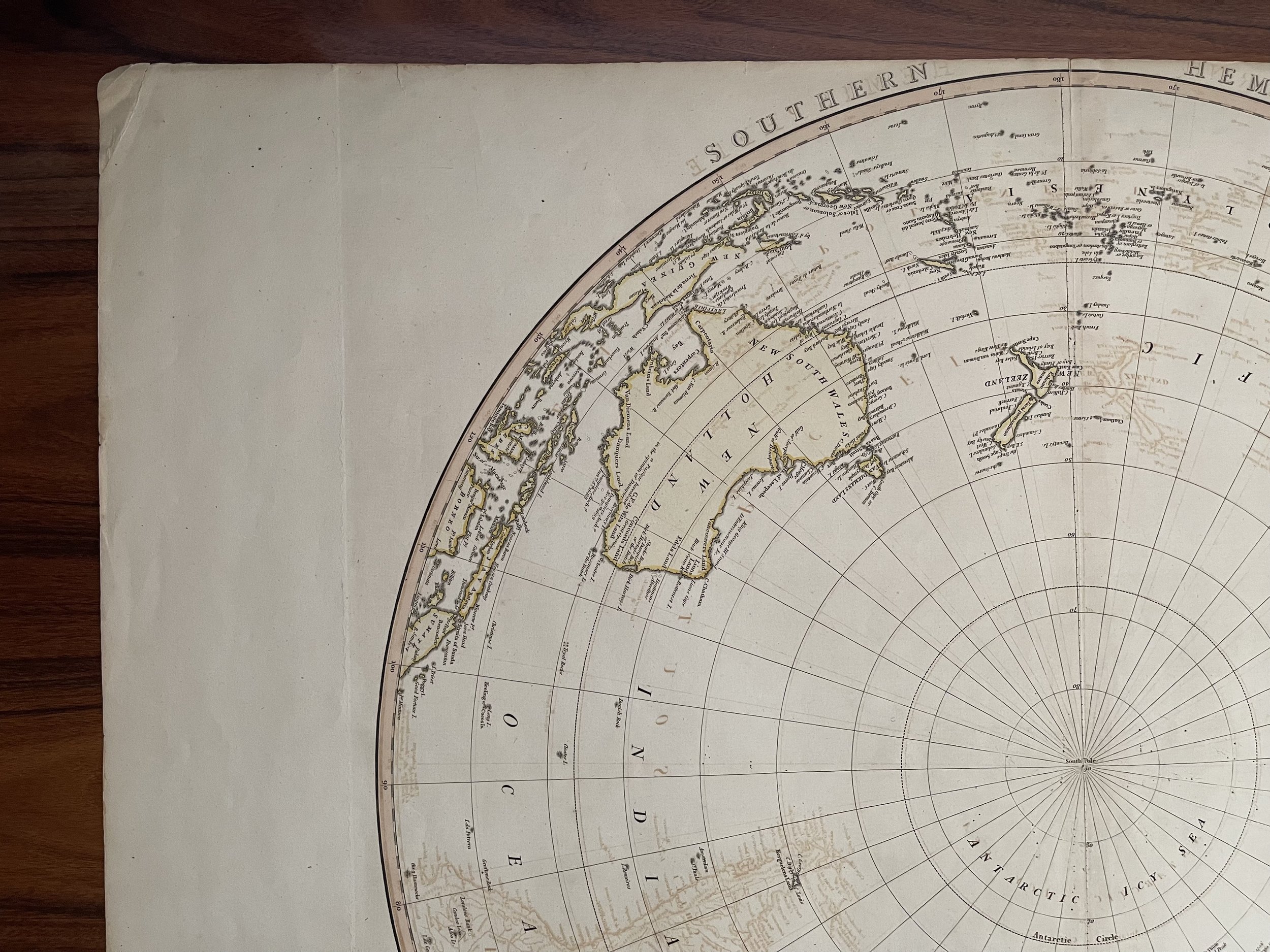 Image 2 of 7
Image 2 of 7

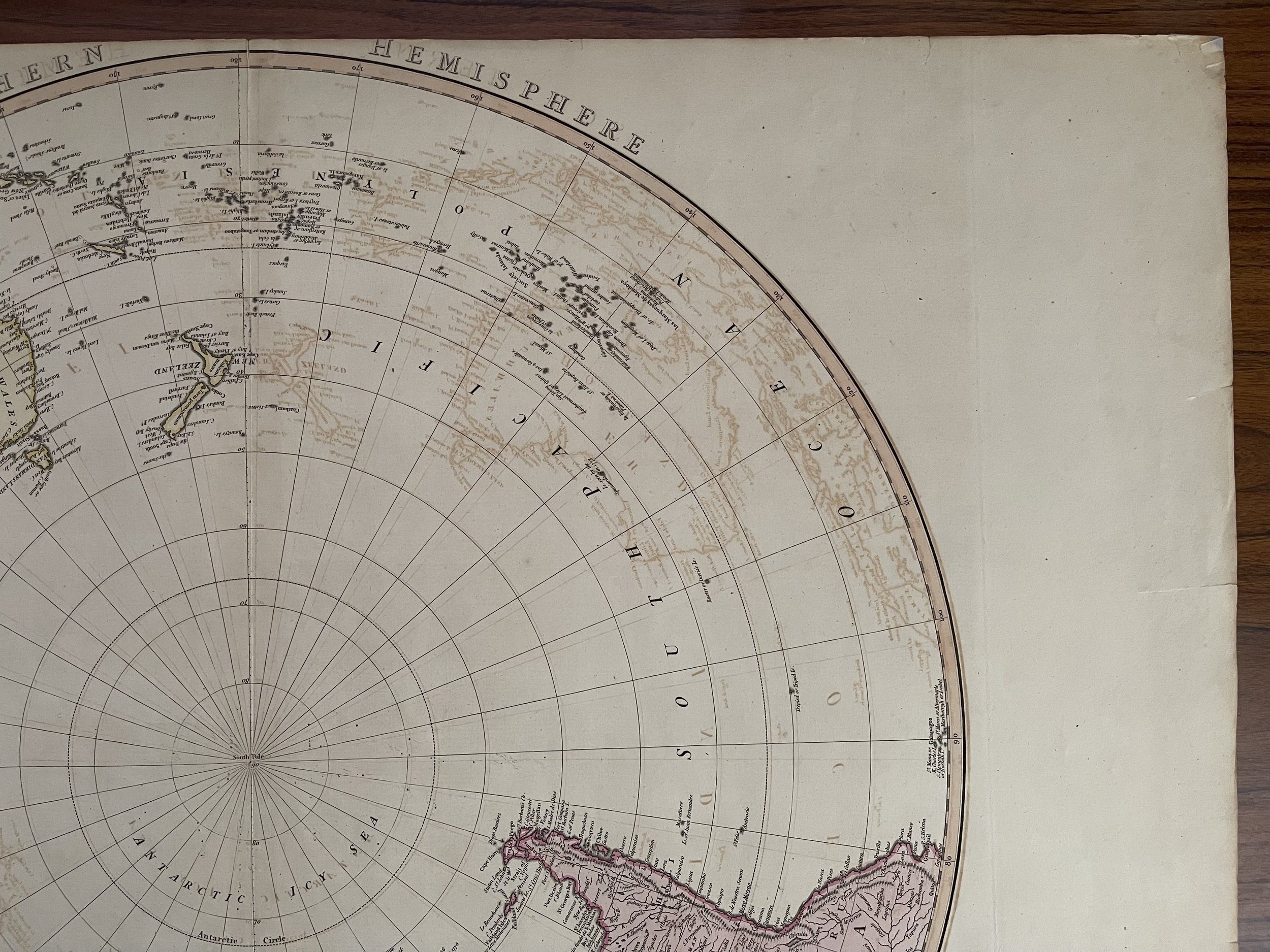 Image 3 of 7
Image 3 of 7

 Image 4 of 7
Image 4 of 7

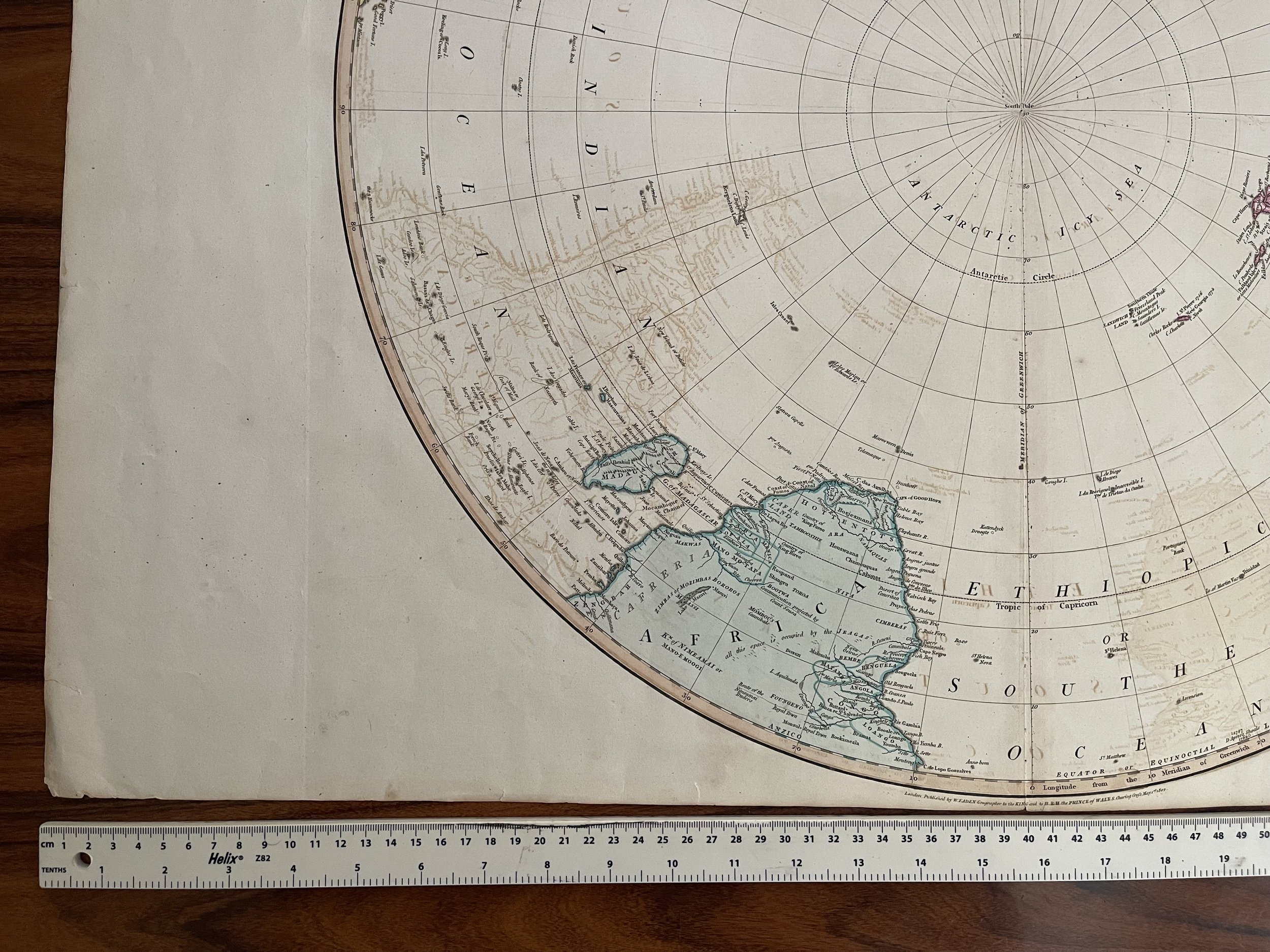 Image 5 of 7
Image 5 of 7

 Image 6 of 7
Image 6 of 7
 Image 7 of 7
Image 7 of 7








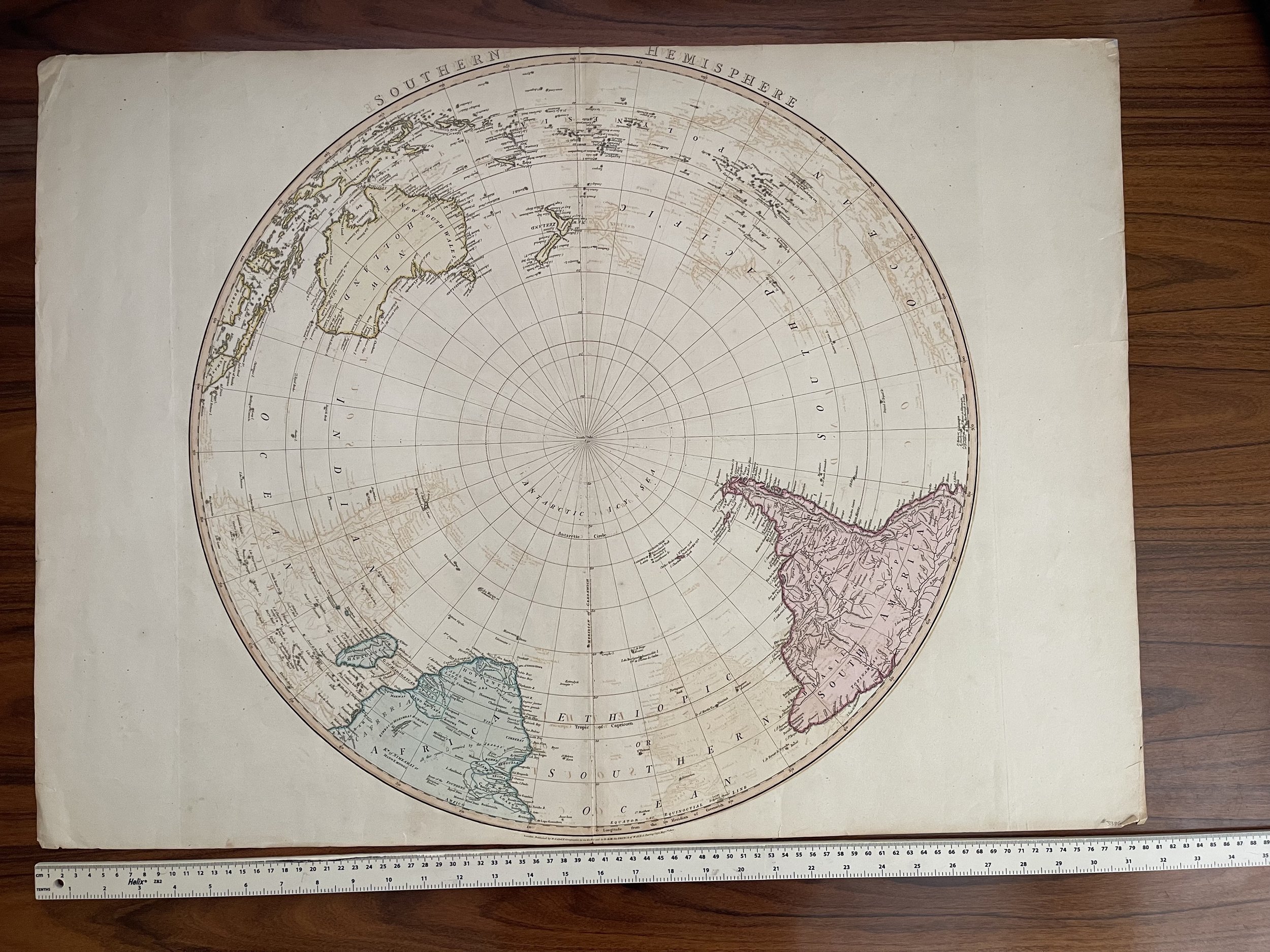
Southern Hemisphere. London, published by William Faden, Geographer to the King and to H.R.H. the Prince of Wales - 1802. Benjamin Baker sculpt.
Very large folio Hemispheric map (very scarce). Full hand col. by continent. Relief on verso.
Tooley, R.V. The mapping of Australia and Antarctica, 2nd. ed., p. 75, no. 560.
William Faden (1749 – 1836) was an English cartographer and a publisher of maps. He was the royal geographer to King George III. He replaced Thomas Jefferys in that role.
The title of "geographer to the king" was given to various people in the 18th century, including John Senex, Herman Moll, Emanuel Bowen and Thomas Jeffreys. All of these men, including William Faden, were engravers and publishers, not scholars or academics. Their part was to publish and supply maps to the crown and parliament.
William Faden (1749-1836) was the most prominent London mapmaker and publisher of the late-eighteenth and early-nineteenth centuries. His father, William Mackfaden, was a printer who dropped the first part of his last name due to the Jacobite rising of 1745.
Apprenticed to an engraver in the Clothworkers' Company, he was made free of the Company in August of 1771. He entered into a partnership with the family of Thomas Jeffreys, a prolific and well-respected mapmaker who had recently died in 1771. This partnership lasted until 1776.
Also in 1776, Faden joined the Society of Civil Engineers, which later changed its name to the Smeatonian Society of Civil Engineers. The Smeatonians operated as an elite, yet practical, dining club and his membership led Faden to several engineering publications, including canal plans and plans of other new engineering projects.
Faden's star rose during the American Revolution, when he produced popular maps and atlases focused on the American colonies and the battles that raged within them. In 1783, just as the war ended, Faden inherited his father's estate, allowing him to fully control his business and expand it; in the same year he gained the title "Geographer in Ordinary to his Majesty."
Faden also commanded a large stock of British county maps, which made him attractive as a partner to the Ordnance Survey; he published the first Ordnance map in 1801, a map of Kent. The Admiralty also admired his work and acquired some of his plates which were re-issued as official naval charts.
Faden was renowned for his ingenuity as well as his business acumen. In 1796 he was awarded a gold medal by the Society of Arts. With his brother-in-law, the astronomer and painter John Russell, he created the first extant lunar globe.
After retiring in 1823 the lucrative business passed to James Wyld, a former apprentice. He died in Shepperton in 1826, leaving a large estate.
Benjamin Baker - Map engraver and publisher. Engraved numerous maps for William Faden and various leading publishers before becoming principal engraver to the Ordnance Survey in 1804. His duties included not only carrying out the more complex engraving but supervising the other engravers and seeing the maps through the press. Baker and his team came to be regarded as "the best topographical engravers in Europe" (Seymour).
Very large folio Hemispheric map (very scarce). Full hand col. by continent. Relief on verso.
Tooley, R.V. The mapping of Australia and Antarctica, 2nd. ed., p. 75, no. 560.
William Faden (1749 – 1836) was an English cartographer and a publisher of maps. He was the royal geographer to King George III. He replaced Thomas Jefferys in that role.
The title of "geographer to the king" was given to various people in the 18th century, including John Senex, Herman Moll, Emanuel Bowen and Thomas Jeffreys. All of these men, including William Faden, were engravers and publishers, not scholars or academics. Their part was to publish and supply maps to the crown and parliament.
William Faden (1749-1836) was the most prominent London mapmaker and publisher of the late-eighteenth and early-nineteenth centuries. His father, William Mackfaden, was a printer who dropped the first part of his last name due to the Jacobite rising of 1745.
Apprenticed to an engraver in the Clothworkers' Company, he was made free of the Company in August of 1771. He entered into a partnership with the family of Thomas Jeffreys, a prolific and well-respected mapmaker who had recently died in 1771. This partnership lasted until 1776.
Also in 1776, Faden joined the Society of Civil Engineers, which later changed its name to the Smeatonian Society of Civil Engineers. The Smeatonians operated as an elite, yet practical, dining club and his membership led Faden to several engineering publications, including canal plans and plans of other new engineering projects.
Faden's star rose during the American Revolution, when he produced popular maps and atlases focused on the American colonies and the battles that raged within them. In 1783, just as the war ended, Faden inherited his father's estate, allowing him to fully control his business and expand it; in the same year he gained the title "Geographer in Ordinary to his Majesty."
Faden also commanded a large stock of British county maps, which made him attractive as a partner to the Ordnance Survey; he published the first Ordnance map in 1801, a map of Kent. The Admiralty also admired his work and acquired some of his plates which were re-issued as official naval charts.
Faden was renowned for his ingenuity as well as his business acumen. In 1796 he was awarded a gold medal by the Society of Arts. With his brother-in-law, the astronomer and painter John Russell, he created the first extant lunar globe.
After retiring in 1823 the lucrative business passed to James Wyld, a former apprentice. He died in Shepperton in 1826, leaving a large estate.
Benjamin Baker - Map engraver and publisher. Engraved numerous maps for William Faden and various leading publishers before becoming principal engraver to the Ordnance Survey in 1804. His duties included not only carrying out the more complex engraving but supervising the other engravers and seeing the maps through the press. Baker and his team came to be regarded as "the best topographical engravers in Europe" (Seymour).
Code : A83
Cartographer : Cartographer / Engraver / Publisher: William Faden / Benjamin Baker
Date : 1802 Approx
Size : Sheet size: 23 X 31.5 Inches
Availability : Available
Type - Genuine Antique
Grading - A-